NATURE OF ECONOMICS
DEFINITION OF ECONOMICS
The term economics is derived from the word “oeconomicus” by Xenophon in 431 B.C. It is derived from two words economy and science. Economy means proper utilization of resources. It means economics is the science of economy or science of proper utilization of resources. It is comprised of theories, laws, principle related to utilization of resources so as to solve the economic problems, satisfy the human wants or need and so on. However, the economics is defined in different ways by different economists.
There are mainly three definitions of economics:-
There are mainly three definitions of economics:-
a. classical or wealth definition (Adam Smith)-1776 A.D
b. neo-classical or welfare definition (Alfred Marshall )-1890 A.D
c. modern or scarcity and choice definition (Lionel Robbins)-1932 A.D
a. classical or wealth definition (Adam Smith)-1776 A.D
The famous classical economist Adam smith for the firs time defined economics as “science of wealth”. The definition was given in the book “an enquiry to the nature and the causes of wealth of nations” published in 1776 A.D. the book is popularly known as “wealth of nations”. According to smith, labor is the main source of income or wealth. More wealth is accumulated only if more labor is used. Economics explains the human behavior and activities they do for wealth. This definition was based upon the assumptions of full employment, perfect competition, no governmental interventions, money just as a medium of exchange and so on.
This definition has following main proposition:-
i. economics is science of wealth
ii. labor is the only source of income
iii. there is perfect competition in product as well as labor market
iv. the government should not interfere the activities of people and business organizations
v. this definition is influenced by physiocracy and mercantilism.
Criticism:-
Wealth definition has over emphasized wealth. Economics is science of human activities rather than only wealth. Adam smith considers only material things or wealth as subject matter of economics but human beings require some immaterial things like self esteem or dignity, social prestige, national identity and so on too. The immaterial things are called essential things for human satisfaction. Wealth definition is based upon the theory of subsistence wage which is known as iron law of wage. The law was against the workers and in favor of employers. Adam smith doesn’t explain about scarcity
of resource and choice of best alternative for the use of resources. The problem of scarcity and choice is burning issue in the modern economics but he fails to explain about the problems of scarcity and choice. The wealth definition is based upon assumptions of full employment and perfect competition but none of these two is in existence. This definition is based upon the assumption of no intervention of government in economic activities of people and business organization but we find in every country more or less governmental intervention.
b. neo-classical or welfare definition (Alfred Marshall )-1890 A.D
In 1890, Alfred Marshall, a famous neo-classical economist and a great contributor to micro economics defined economics as the science of material welfare. Here, the material welfare means the quantities of physical goods consumed by people. if the people are consuming large quantities of goods, they are said to have high level of welfare into two types
1. material welfare
2. immaterial welfare
According to him, only the material welfare is the subject matter of economics. He assumes every person is rational and s/he uses the resources in his/her possession very properly so as to maximize their own welfare. Economics is therefore the science that studies the rational behavior revealed by the people. Major propositions of Marshall’s welfare definition are:-
1. Economics is science of material welfare
2. Economics is social science i.e. science of mankind
3. Economics is the study of rational behavior of people revealed for maximization of material welfare.
Criticisms:-
This definition of economics a science of material welfare was assumed correct until the arrival of Lionel Robbins. He criticized the definition under the following aspects:-
1. Classificatory activities of Marshall into material non material welfare, economics and non economic goods is only classificatory not analytical because single human cannot be material as well as non material according to the nature and purpose of work.
2. Non material activities like feeling of social service, human desire also satisfy human needs. This idea has not been prioritized
3. Non welfare consumption like harmful drugs, tobacco, and alcohol don’t promote social welfare but still are in the study of economics
4. Economics should study about total human beings but wealth definition doesn’t study about isolated people like saints, nuns, monks etc.
c. modern or scarcity and choice definition (Lionel Robbins)-1932 A.D
According to Lionel Robbins, economics is the science of scarcity of the resources and the choice of best alternative for their utilization. The resources are limited in supply. Each resource is usable for different purposes. The wants or need of people are unlimited. The wants differ in importance. They differ from place to place, from time to time and from person to person. Some wants are more important whereas some are not. All wants cannot be fulfilled because of insufficiency of resources. Therefore, we have to go on utilizing the resources in such a way, so that, our more wants can be fulfilled leaving no one in most important wants unfulfilled. For it, we must select best ways for the utilization of the resources. We should have the complete information of resources available, needs of the country and their importance and ways for the utilization of resources. This definition is given in 1930 A.D after WWI. During third decade of the twentieth century, the European countries were badly in need of large quantities of resources for rehabilitation, construction of infrastructures, renovation etc. they were destructed in war. This definition is both normative and positive in nature. The major propositions are:-
1. there is unlimited human needs or wants
2. there is scarce means of resources
3. there are alternative use of resources
4. there is need of choice
Criticisms:
The definition is criticized in the following ways:-
1. economic problems arises not only due to scarcity but due to under, miss or over utilization of resources
2. economic problems arises due to inequality too
3. there is political consideration
4. needs and resources may vary
Superiority of Robbins definition over Marshall’s definition:-
1. the definition is scientific
2. the definition is universally accepted
3. the definition has wide scope
4. the definition has science of choice
Microeconomics:-
The term microeconomics is derived from the word micro economy and science. The term micro is also derived from the Greek word micros which means small or tiny. Microeconomics is defined as the science of small or tiny part of the economy. It provides us the detail information of microeconomics units. The units are single consumer or consumer of a firm or an industry. A single firm or firms belonging to an industry is called worm’s eye view of an economy. In microeconomics we study about the relationships between microeconomic variables like utility, cost of purchasing, demand, supply, price, cost of production, and revenue from sale, profit or loss and so on, it is the study of behavior of consumers and firms.
Scope of microeconomics:-
The scope of microeconomics means its subject matter. it means area of application too. The scopes are:-
1. study of consumers behavior
-cardinal utility theory
- ordinal theory
-revealed preference theory
-cardinal behavior theory
2. Study of production and cost function
Mathematically.
Q=output (quantity)
C=cost of production
K=capital
Q=f (K and other inputs)
C=f (Q)
Therefore, C ∞ input
3. Study of price and output determination
Profit=revenue-cost
Markets = monopoly, duopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition and perfect competition
4. Study of microeconomic distribution
Factors of production-land, labor, capital and organization
Factor wages-rent, wage, interest, profit
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is derived from the word macro, economy and science. The term “macro” is also derived from Greek word “macros” which means large or big. Therefore, macroeconomics can be defined as the science of large segment of the economy or economy as a whole. It provides bird’s eye view of the economy. It gives general features of the economy. It is study of features of economic problems, causes and remedies of the problems in different sectors. The sectors are divided into household sectors, government sector, foreign trade sector, business sector. In macroeconomics we study about the relationship between macro economic variables, the variables are:
a) Aggregate consumption
b) Aggregate income
c) Aggregate saving
d) Aggregate investment
e) Aggregate demand
f) Aggregate supply
g) Price level
In macroeconomics we study about the causes and remedies of trade and payment, price instability, Inequality etc
Scope or subject matter of macroeconomics:
Scope means the subject matter. It means the area of application...
1. Study of wage level and employment level
The macroeconomics deals with wage level and employment level. The level of employment depends upon demand for labor and supply of labor. Both of these factors depend upon wage level. There are different theories of employment like classical theory, Keynesian theory, Kaltorian theory and other modern theory
2. The study of price level and output level
Macroeconomics is concerned with determination of equilibrium price level and output level. The price level means average of the prices of goods and services bought and sold in the country in a year. The level of output depends upon aggregate demand and price level. There are different theories of determination of price level and output level. Among them, Keynesian theory of effective demand is very popular. The theories are the subject matter of macroeconomics.
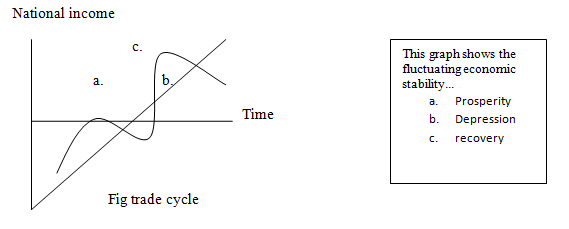
3. The study of trade cycle
Macroeconomics is concerned with trade cycle too. It explains how the economics ups and downs
occur, what are their causes, how the country can overcome fluctuation. There are different theories of trade cycle. Some of them are Schumpeter theory, Hessian theory, Calder’s theory etc.
occur, what are their causes, how the country can overcome fluctuation. There are different theories of trade cycle. Some of them are Schumpeter theory, Hessian theory, Calder’s theory etc.
4) Study of macroeconomic distribution
The macroeconomics is the study of distribution of income, wealth or resources in the country among the people. It is the study of different theories, laws and principles of distribution of income in the form of wage, interest, profit and rent. It gives us knowledge of effects of high inequality in the distribution of income and wealth. It gives us remedies of unequal distribution and the economic problems due to the inequality.
Normative or positive economics
Economics is both positive and normative science. It is the study of facts as well as ideal theories and principles too. It can be explained as following:
a) Positive economics
Economics is positive science. It is the study of facts or things in reality or existence. In economics the large number of economic problems or questions like what are produced, how goods are priced and distributed, how much profit is earned by firms, what different type of resources are available, hoe the resources are utilized, who are performing different economic activities, why the economic problems are occurring, why is the country suffering from unemployment, price instability, economic instability, import dependency and so on are put and answered. There are different theories laws and principles based upon facts we study in economics. That’s why economics is called positive science
b) Normative economics
Economics is normative science. It is the study of things ought to be. In economics, we study different ideal theories and principles. They are concerned with different economic problems. They give us ideas for overcoming of different economic problems. They are helpful to formulate proper policies and plans. They are helpful to solve the problems of unemployment, import dependency, improper allocation of resources, price and economic instability, unequal distribution of income and wealth and so on. Economics helps us to decide how much goods should be produced, hoe much they should be priced, hoe the government should control money supply, interest rate, public debt, government expenditure etc , how the consumer should allocate the money to get maximum satisfaction from the expenditure, how the firms should combine the inputs to earn maximum profit and so on. This all have ethical importance. That’s why economics is call normative science.
Economics is a science or an art
Economics is both art and science. It is called a science because it is the scientific study of relationships between economic variables, behavior of consumers and firms, nature of market and economy, effect of change in one or more economic variables on the others and so on. The different theories, laws and principles are studied in economics. All of them are generalized and simplified on the basis of facts so as to make them easily understandable. Therefore, economics is said to be science.
Economics is an art. The different theories, laws are explained with the help of graphs, figures, tables, charts, equations etc simplifying and generalizing them. Simplification is to make them easily understandable and generalization is to make them applicable to all economies. In order to explain theories, laws and relationships between economic variables we make some assumptions. The assumptions define the conditions for the application of theories, laws and\d the relationships. That’s why economics is an art.
Importance of microeconomics:
1. Important to the consumers
Microeconomics provides the ways for proper allocation of money on different goods and services so that they can get maximum utility. There are different theories of consumers behavior, the theories explain how the consumers should spend the limited money they have to maximize their satisfaction
2. Important to the firms or businessmen
The firms or businessmen use the microeconomic theories of consumer behavior, production, cost, market, revenue and so on to make proper economic decisions. The microeconomics helps them to know the purchasing power of ability to pay, proper combination of inputs to maximize cost or maximize profit, effects of change in tax rates, subsidies and so on
3. Important to the government
Government can determine taxes, subsidies, wage level, allowances etc on the basis of effects of change in these factors on the demand for goods and services. Some goods are levied while some are subsidized. The salaries and allowances are adjusted on the basis of relationship between these variables and demand. Interest rate, exchange rate and money supply too are changed with the help of microeconomic theories.
4. Important for the study of other economic science.
Microeconomics helps us to study of other economic sciences like macro economics, public finance, monetary economics, labor economics, and international trade economics and so on. The theories and laws of these economic sciences are based upon micro economics theories and laws.
Importance of macroeconomics
1. To know the relationship between macro economics variables:
The macroeconomics helps us in the study of relationship between large numbers of macro economics variables. The variables are Aggregate consumption, Aggregate income, aggregate saving, Aggregate investment, Aggregate demand, Aggregate supply, Price level
2. To know the functioning of economy
Macroeconomics helps us to know how the economy functions, how it is regulated, For it macro economics provides us the knowledge of product market, labor market, capital market, land market, international trade market etc. it in forms us the country can achieve equilibrium only if all of the markets are in equilibrium.
3. To correct unfavorable balance of trade and payment
Macroeconomics provides us different theories of international trade. It provides us different remedies of import dependency and greater outflow of money from the country. The government or country may adjust custom duty, exchange rate, transaction of gold etc to promote export and to reduce import.
4. To achieve high economic growth and employment level
With the help of theories and models of economic growth and employment we can induce investment increase in income and employment opportunities
Thus, these are the importance of micro and macro economics.
Read more: http://www.hsebguides.com/2012/07/nature-of-economics-class-xi-economics_28.html#ixzz2IEQ14UzI
Comments